Fixed Length Parser
Fixed Length Parser processes a stream of fixed length data as an input and give elements as parsed output. This is useful when the source data is in text format (information is contained in a single field) and it needs to be put into multiple fields for further integration.
In this document, we will learn how you can use Fixed Length Parser in Astera.
Sample Use-Case
The sample data that we are using is a fixed length text file containing customers’ information.
Observe that all the information such as name, street number, street type, city, state, and zip code are concatenated in a single field. We want to parse the Contact_Details field into Name, Street Number, Street Type, and other respective fields.
To parse the data into separate fields, we will use the Fixed Length Parser object in Astera.
Extracting Data
To parse the data, we first have to extract it. Since the data is stored in a continuous stream, can not extract it directly using a Fixed Length File Source object. Therefore, we will use a combination of transformations to get the desired outcome. The diagram below explains the process that we’ll be following, right from extraction to to parsing the data.
Let’s begin with extracting the data.
Go to Toolbox > Transformations > Constant Value and drag-and-drop the Constant Value object onto the designer.
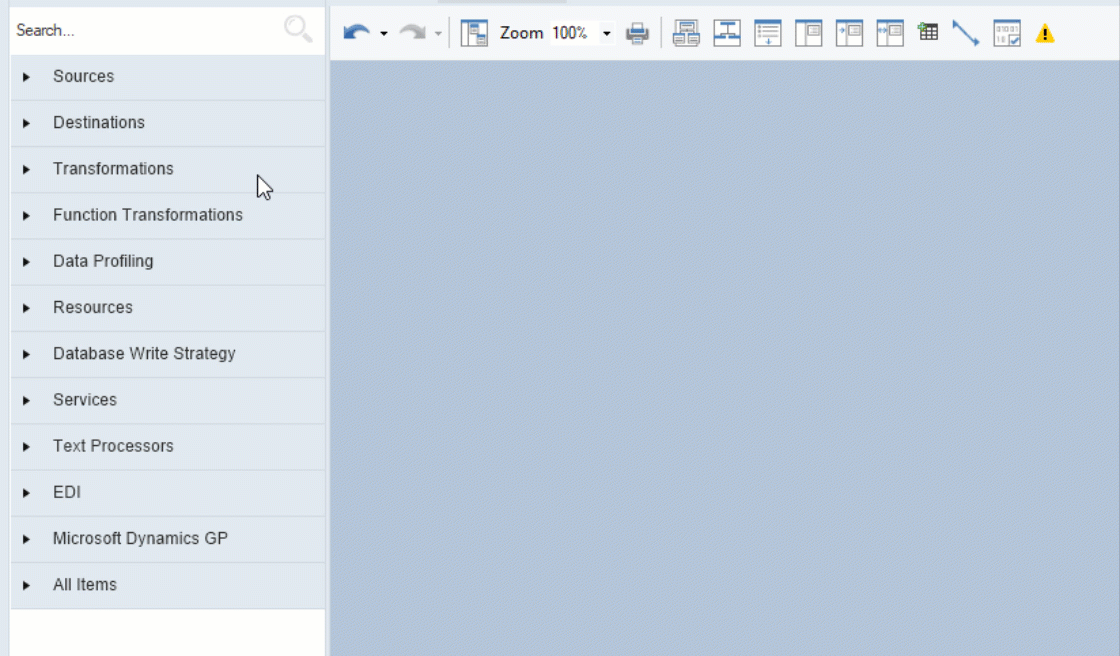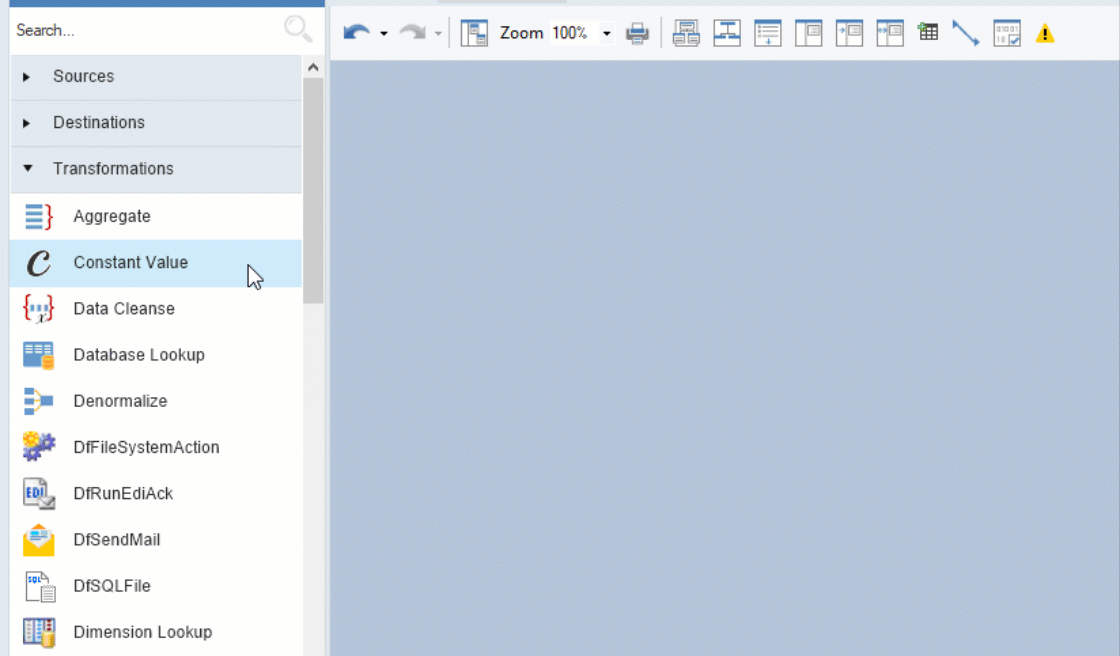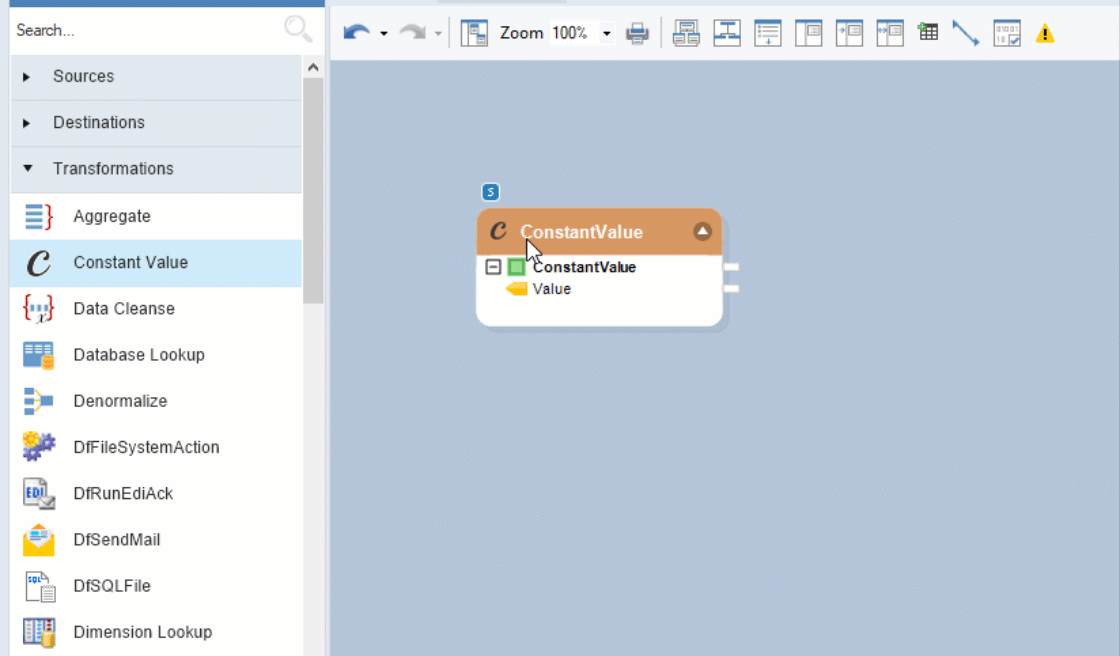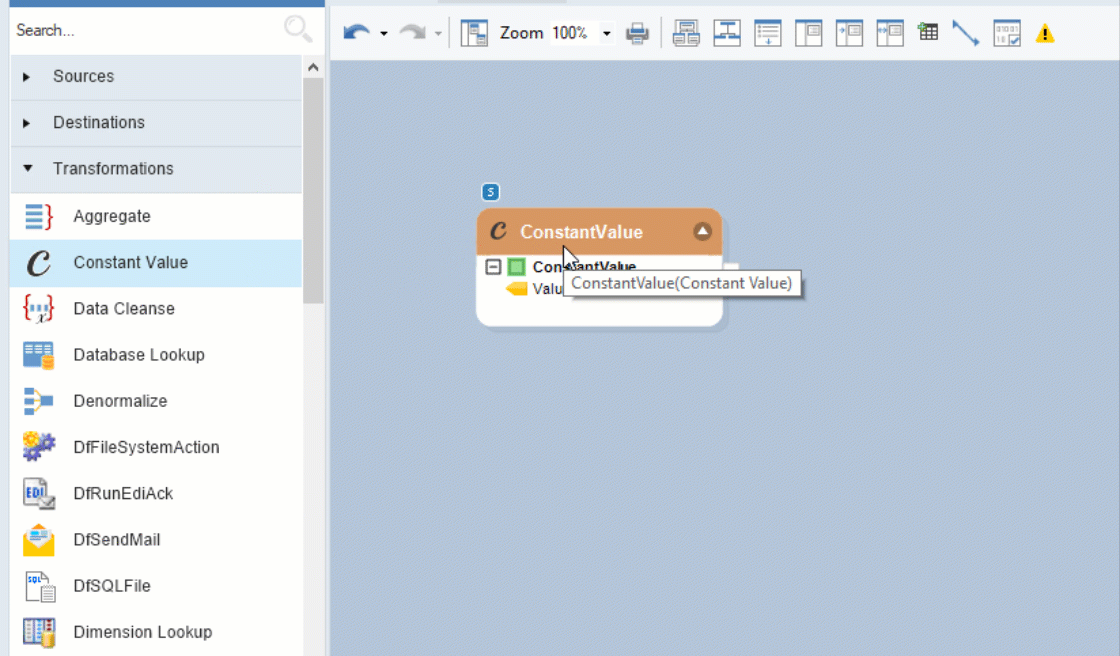
Right-click on the object’s header and select Properties from the context-menu.
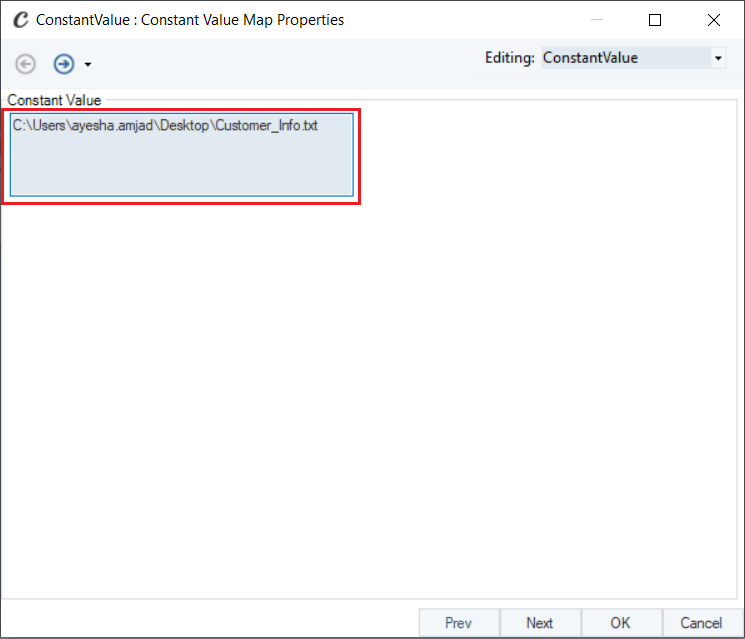
In the Constant Value field, provide the file path of the source file (file containing customers data in a stream). Click OK.
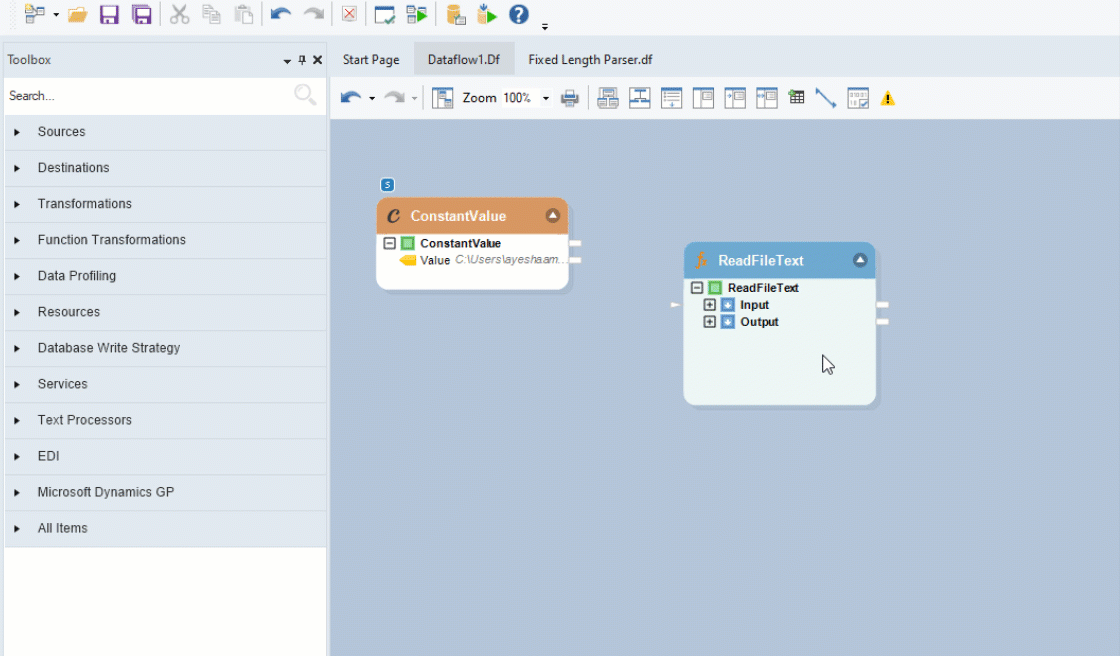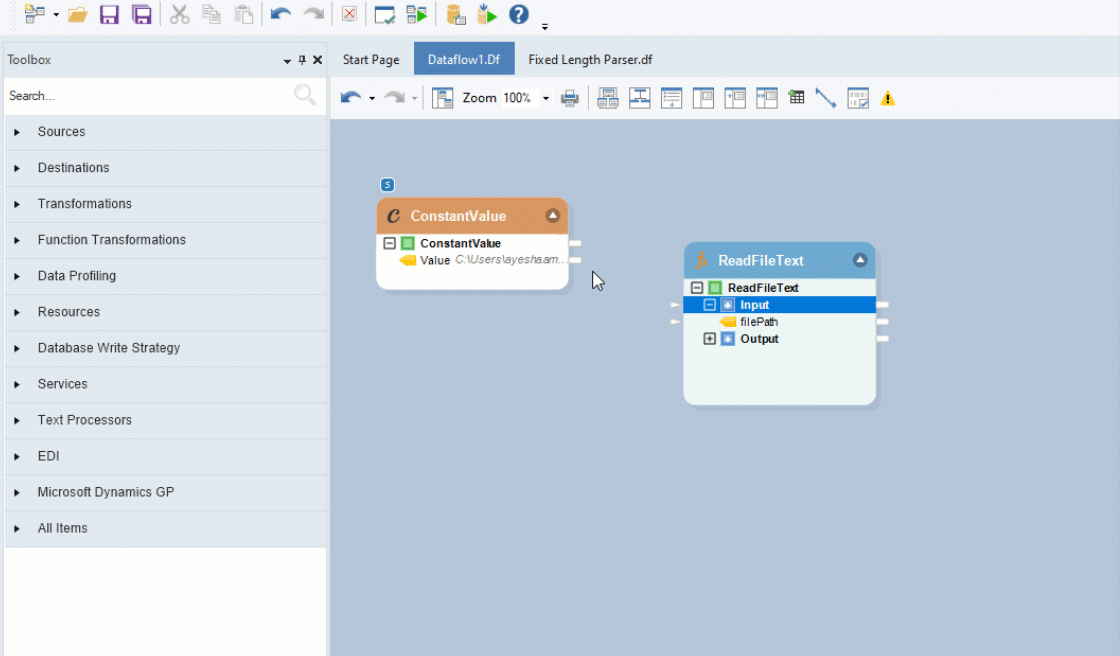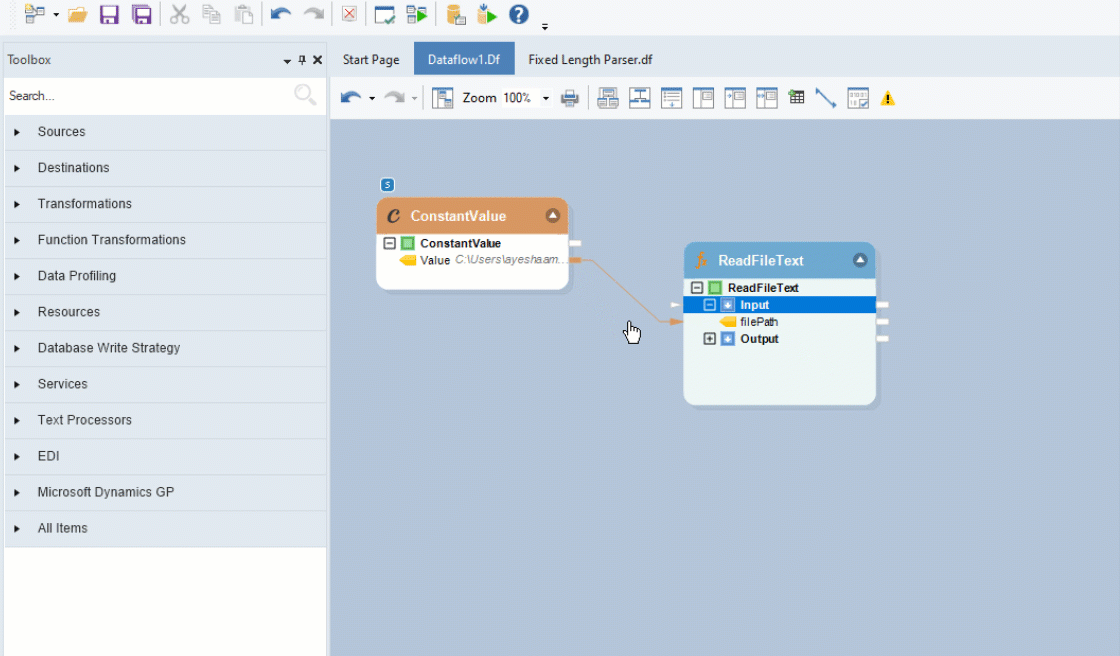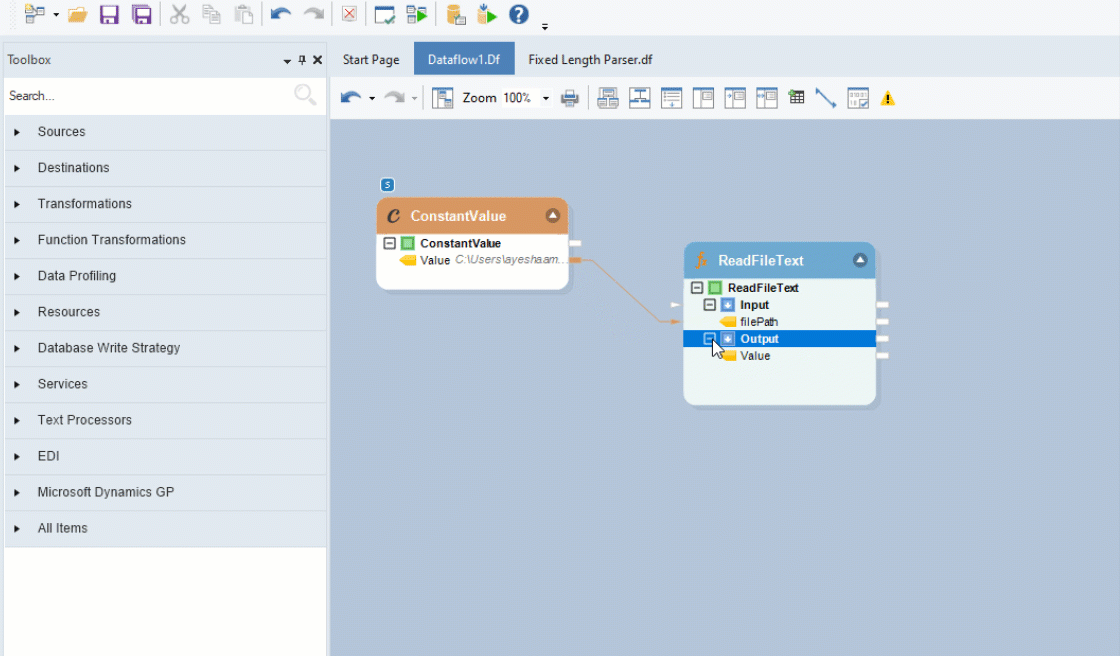
Next, go to Toolbox > Function Transformations > Files > ReadFileText(String filePath) - String, and drag-and-drop the object onto the designer.

You an see that the dragged transformation object has two sub-nodes - Input and Output.
Expand the Input node and map the Value field from the Constant Value Transformation object to the filePath field inside the Read File Text object.
This will redirect Astera to read the data from the given file path. Now we can use the Fixed Length Parser object to parse the text data into separate fields.
Using Fixed Length Parser
To get the Fixed Length Parser object, go to Toolbox > Text Processors > Fixed Length Parser and drag-and-drop the object onto the designer. Map the Value field, under the Read File Text object, onto the Text field inside the Fixed Length Parser object.
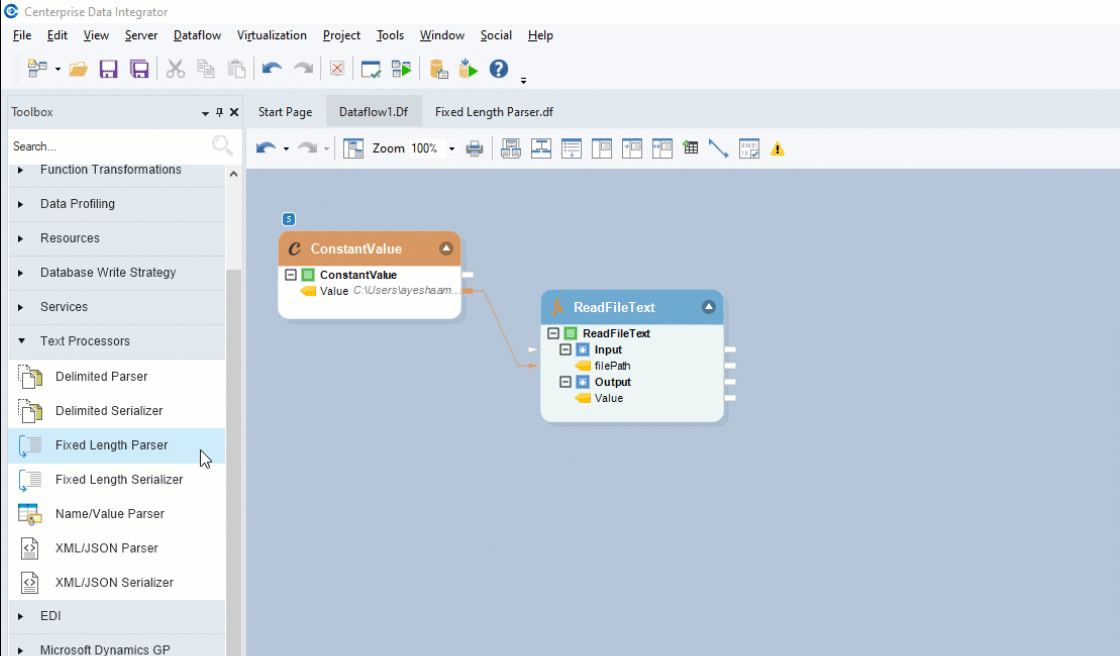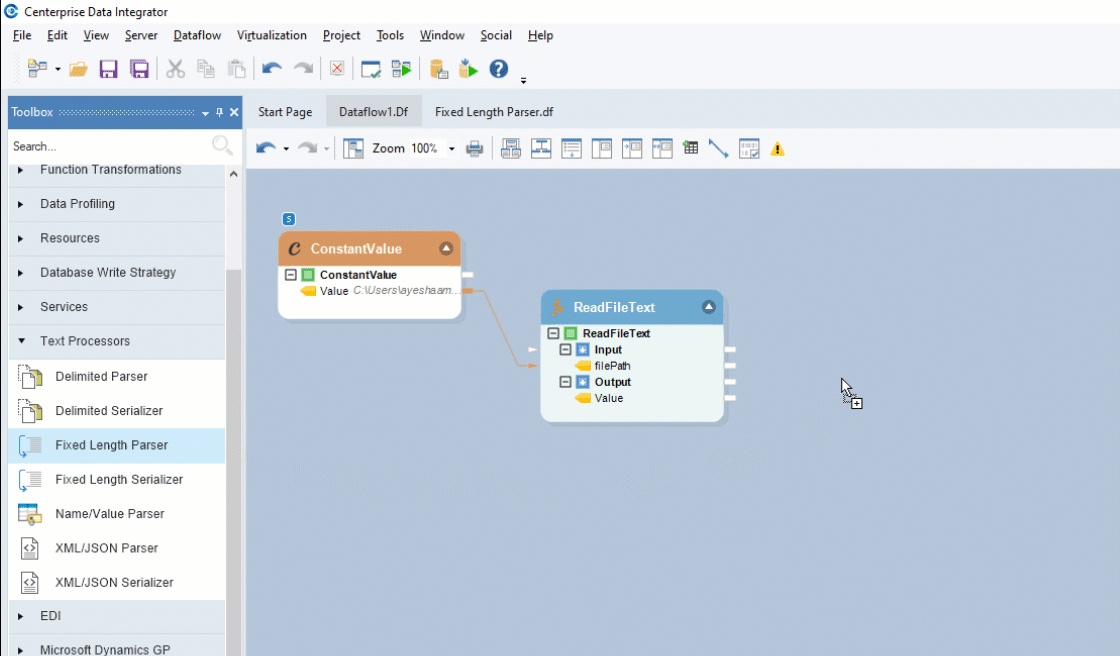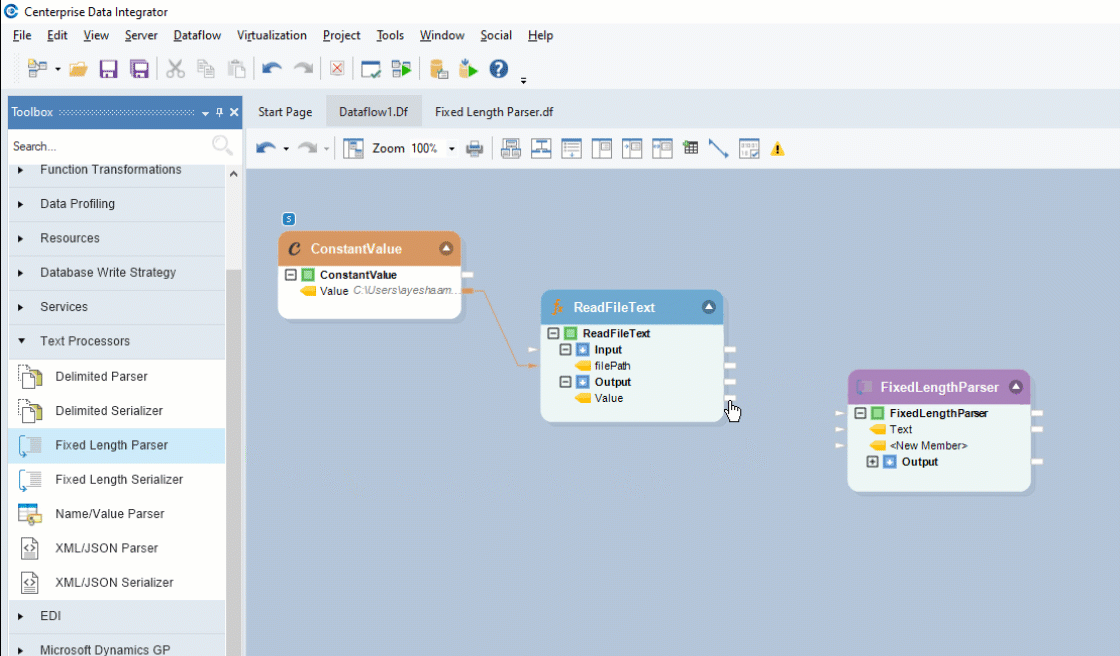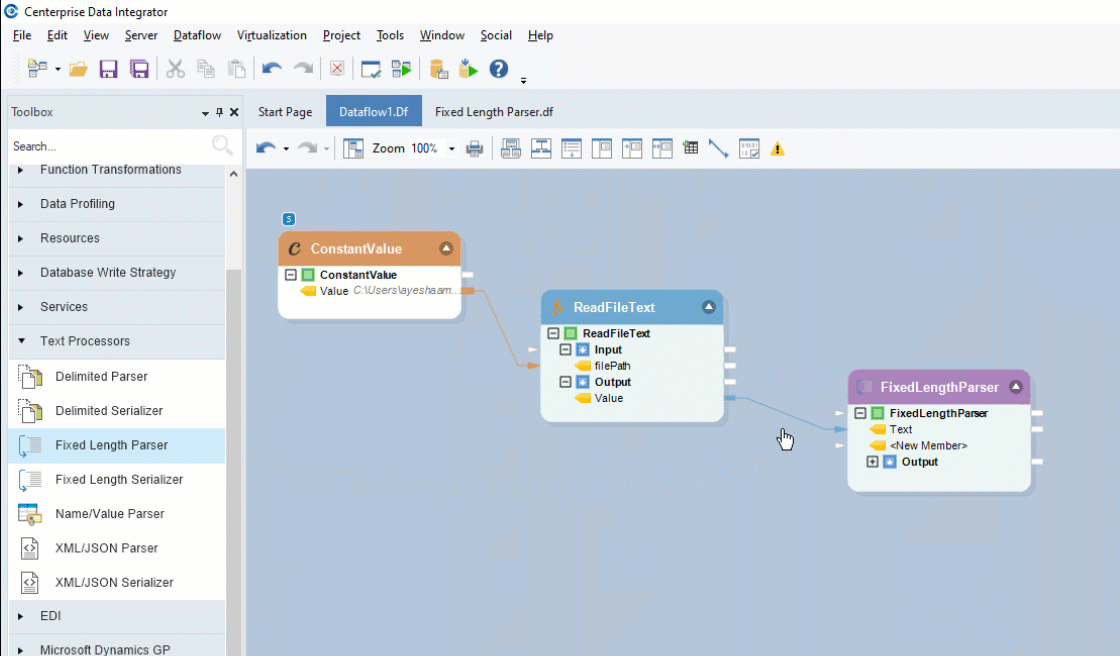
You can see that the dragged-object also contains an Output sub-node which is currently empty.
Configure the Fixed Length Parser object by right-clicking on its header and selecting Properties.
A properties window will open. Here you will see three options, make sure the first two options are checked.
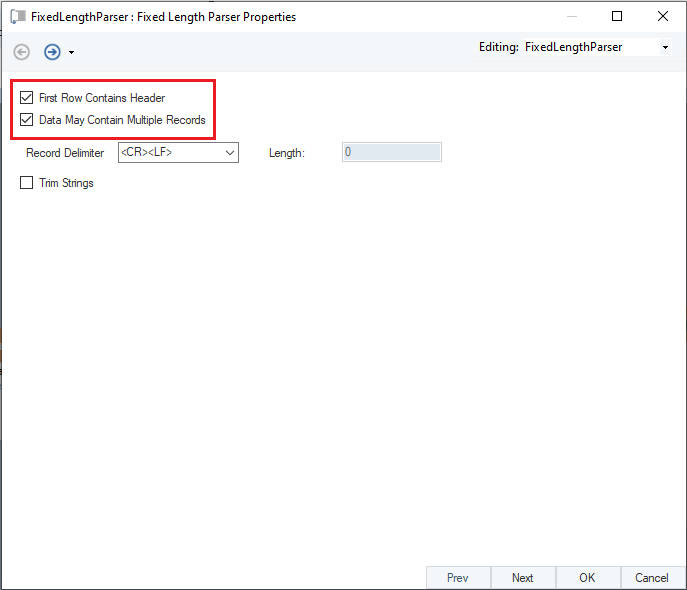
Click Next, and you will be directed to a Source Fields window.
Here, you have to provide the name of each field that you want to parse the source date into, as shown below.
Click OK. Now, expand the Output node inside the Fixed Length Parser object. You will see all the fields that you have created in the previous step.
Right-click on the object’s header and select Preview Output from the context menu.
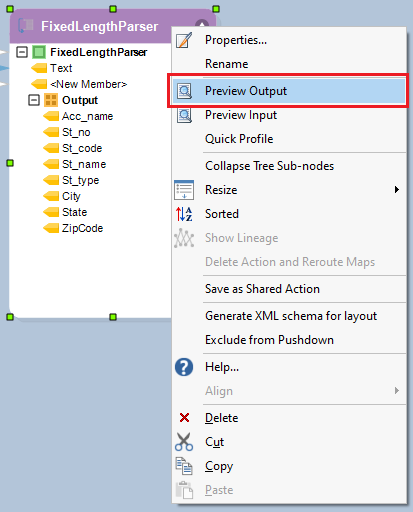
A Data Preview window will open. Expand the nodes, and you will see a parsed output of each record.
To store this parsed output, write it to a destination file.
Writing to a Destination
Right-click on the Output sub-node inside the Fixed Length Parser object, and go to Write to > Excel Workbook Destination. An Excel Workbook Destination object will be added to the dataflow designer with auto-mapped fields.
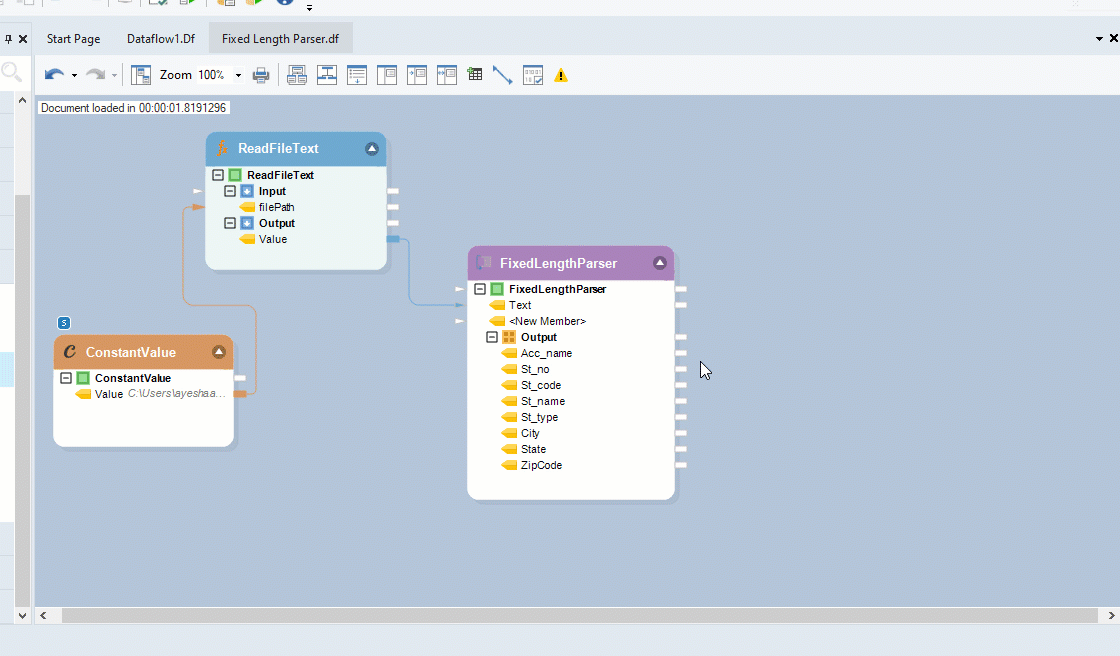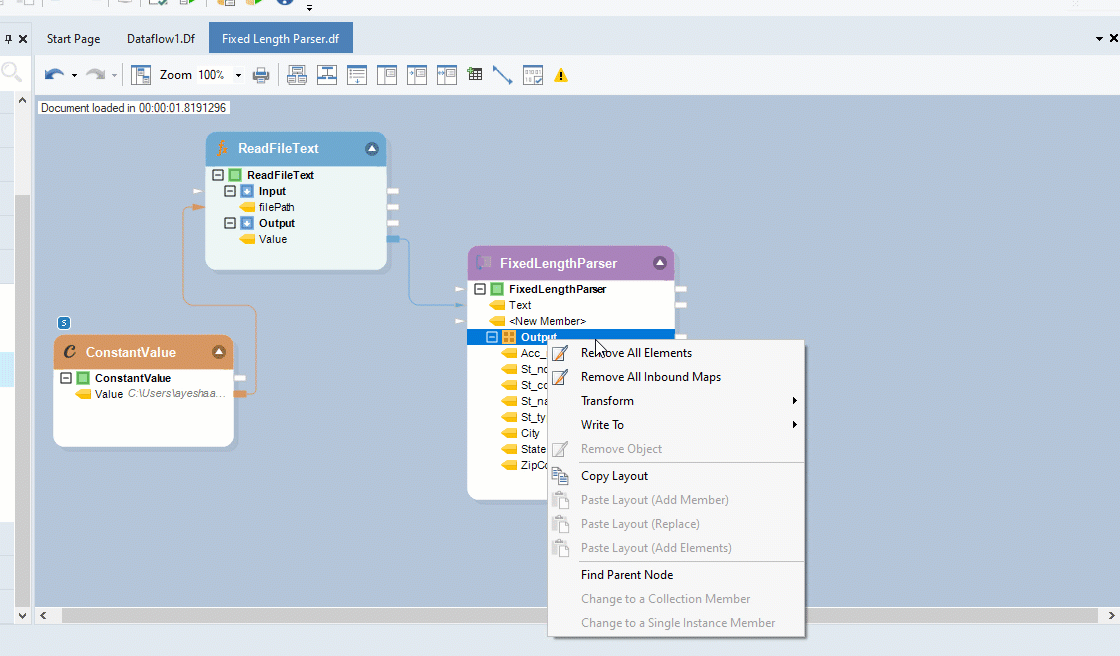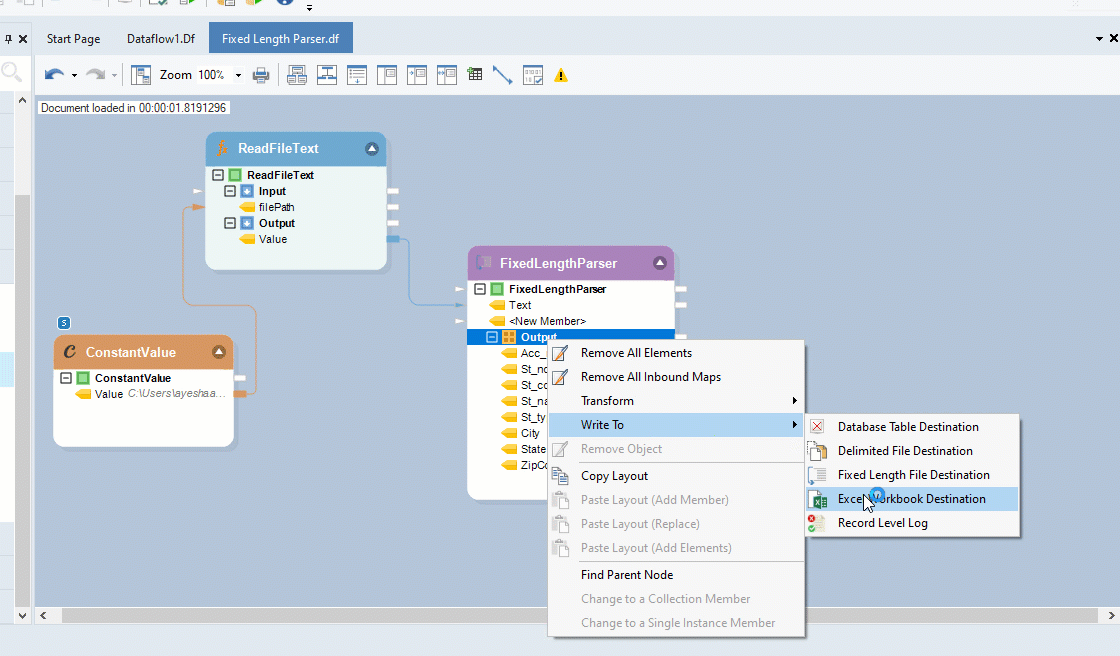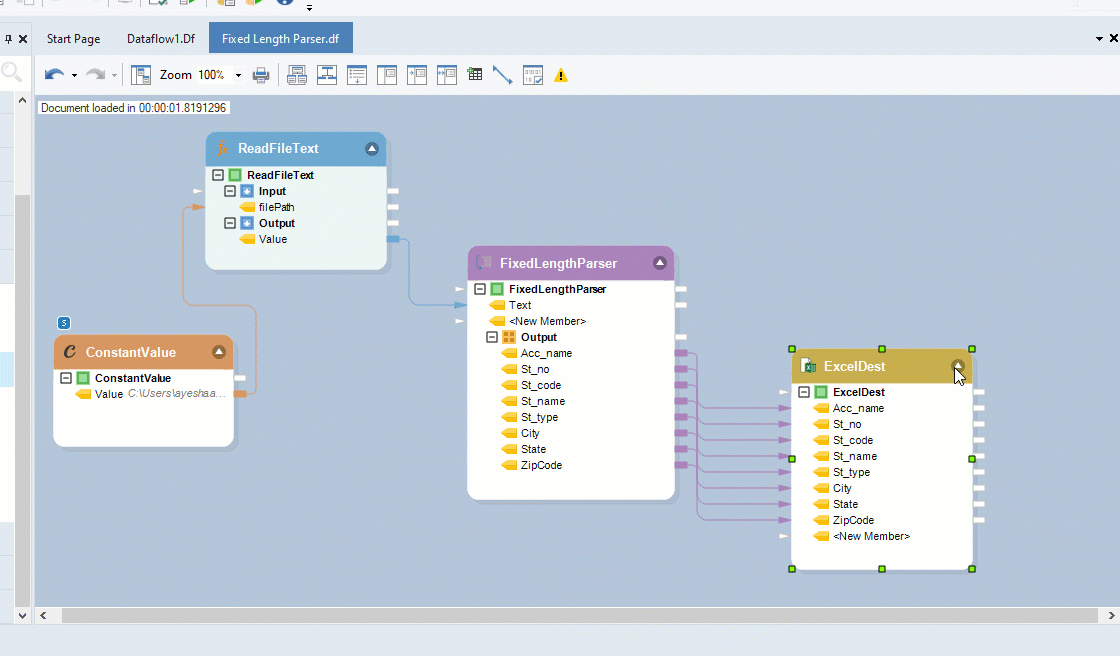
Configure settings for the Excel Workbook Destination object.
Learn how to configure settings for Excel Workbook Destination from here.
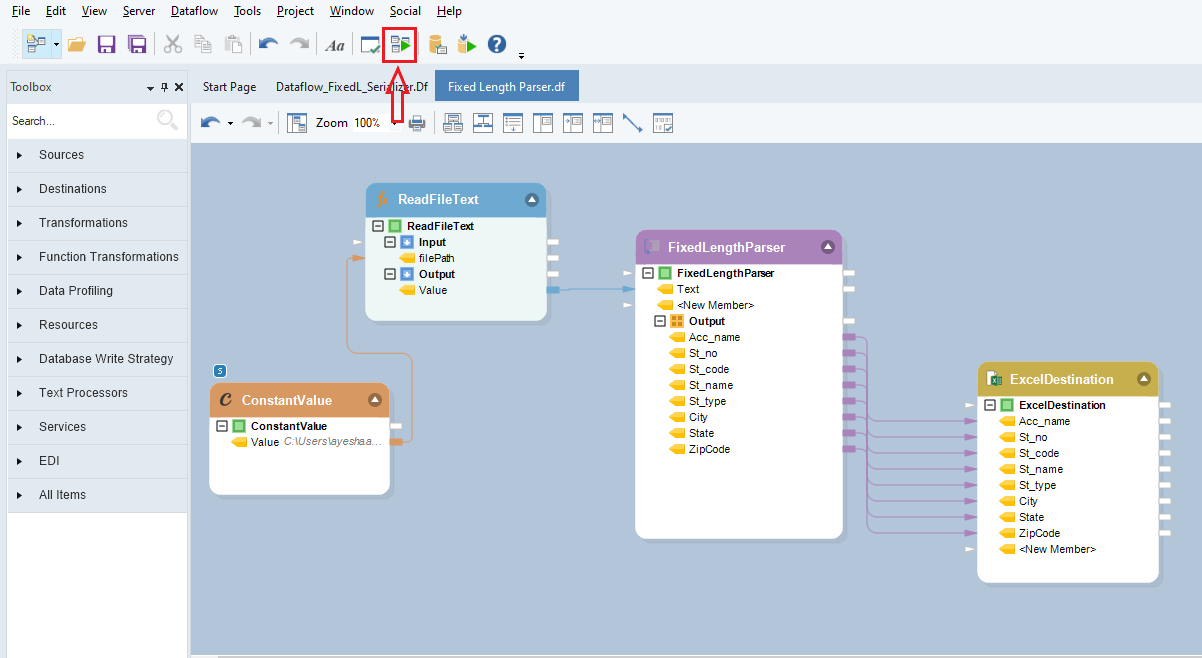
Click on the Start Dataflow icon, located in the toolbar at the top, to create this destination file.
Was this helpful?